Happy Independence Day!
Team of Zappy Consults wish you all a very happy Independence Day!
In a liberalised nation like India, people always think to escape from the little mandatory restrictions that they have to follow. Is it easy to escape from the mandatory compliances? Will it cost anything by avoiding certain mandates? Come let’s see in the below section. The Legal Term for the month and the summary of Notifications by MCA, SEBI, RBI and IT Department will follow the article as always.
![]() Saranya Deivasigamani,
Saranya Deivasigamani,
CEO
Effect of Non-Compliance
We have many of our clients asking – Can we skip this compliance? Can we skip this payment? We have not started any business till date do we still need to make this payment? Everyone are interested in getting away from the compliance and many are not aware what all compliances are mandatory for them and what are not.
In this section, we would see what are all the adverse effects of non-compliance of all mandatory compliances that a Company or LLP should do every year.
Income Tax Compliances
Every Company and LLP should file the Income Tax Return every year disregards with the Income Tax is paid (payable) or not, business carried or not, income earned or not. The Income Tax Department has taken efforts to identify the non-filers and certain action against them. Let us see what are the compliances and the effect on non-compliance under Income Tax.
The Income-Tax Department has implemented the Non-Filers Monitoring System (NMS) as a pilot project to prioritise action on non-filers with potential tax liabilities. The number of non-filers has been thrown up by NMS. The Non-filers Monitoring System (NMS) is a pilot project to prioritise action on non-filers with potential tax liabilities. Data analysis was carried out to identify non-filers about whom specific information was available in various sources such as Annual Information Return (AIR), Centralised Information Branch (CIB), TDS/TCS Statement, etc. The identified non-filers are informed by SMS, e-mails and letters in batches. Every LLP have to file the Income Tax Returns for the year. In simple words LLP is a separate legal entity so with the partner’s income tax return has to file the LLP Income tax return. It is a form where they show the LLP Income and calculate the tax liability & pay the taxes to the government of India. LLP have to calculate their tax liability from their financial statements for the year. Mostly Income Tax Return the last date is 31st July in this year for the Individual and legal entities but in the case where Audit is required, the last date for filing Income Tax returns is 30th September. If the LLP has not carried any business during the year ended, the LLP has to file a NIL IT RETURN with Income Tax Authorities.
Filing the income tax return after the due date invites some consequences which are as follows:
- In case there are some taxes yet to be paid, the filing of income tax return after the due date will attract interest @ 1% per month and part thereof up to the date of filing of the return, on such unpaid tax amount. This interest will be charged only if there is any tax payable.
- A Company will not be allowed to carry forward certain losses if they are filing the income tax return after the deadline.
- A Company may lose interest on refund u/s 244A as delay in filing is attributable for the period by which they have filed a late return.
- A Company may be charged a penalty of
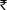 . 5,000 if file the income tax return after the expiry of one year of the financial year for which they are filing the income tax return.
. 5,000 if file the income tax return after the expiry of one year of the financial year for which they are filing the income tax return. - Late returns are not allowed to be revised as compared to a return filed on time which can be revised indefinite times. So late returns are required to be filed with extra consciousness.
ROC / ROS Compliances
Every Company and LLP should file its Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss, Cash Flow and Annual Return to the Registrar of Companies (ROC) or the Registrar of States (ROS) where it was registered through Ministry of Corporate Affairs’ website.
The Consequences for not filing annual return was serious. If a Company fails to file its annual return, it is punishable with a fine which shall not be less than ![]() . 50,000 but which may extend to
. 50,000 but which may extend to ![]() . 5 lakhs. Also, every Director of the Company who is in default shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to six months or with a fine which shall not be less than
. 5 lakhs. Also, every Director of the Company who is in default shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to six months or with a fine which shall not be less than ![]() . 50,000 but which may extend to
. 50,000 but which may extend to ![]() . 5 lakhs, or both.
. 5 lakhs, or both.
If the annual return of a Company is not filed continuously for three financial years, then any Director of such Company would be disqualified and would not be eligible for appointment as a Director of any other Company for a period of five years from the date on which defaulting Company failed to file annual return.
In addition to above, to ensure proper Corporate Governance and Compliance if provisions of the Companies Act, the following action would be implemented:
- No other e-filing of the Company would be accepted by ROC from Director of defaulting Companies for any other Company also.
- Company Secretaries and Auditor of defaulting Companies would not be allowed to sign and certify the filing with the MCA-21 system, till the defect is rectified.
- Members of ICSI, ICAI, and ICWAI must not issue any certificates to such defaulting Companies.
- Action will be taken against defaulting Companies and their director in default in coordination with RBI and SEBI.
If there is a delay in filing form no.8 and 11 of LLP, then LLP will have to pay a penalty as applicable on today’s date. If the filing is not done within stipulated time, there is a penalty of ![]() . 100 per day till it complies. LLP cannot close or wind up without filing Annual Accounts. So if LLP doesn’t file on time, then LLP turns into unlimited statutory liability till the day it complies.
. 100 per day till it complies. LLP cannot close or wind up without filing Annual Accounts. So if LLP doesn’t file on time, then LLP turns into unlimited statutory liability till the day it complies.
The provisions of the Act require LLPs to file the documents like Statement of Account and Solvency (SAS) and Annual Return (AR) i.e. Form 8 and Form 11 within the time specifically indicated in relevant provisions. The LLP Act contains provisions for compounding of offences which are punishable with fine only.
Further, for defaults/non-compliance on procedural matters such as time limits for filing requirements provisions have been made for charging default fees (on daily basis) in a non-discretionary manner. To avoid all the dangerous consequences of heavy penalty, it would be advisable to comply on time within stipulated due date of filing.
If the Limited Liability Partnership fails to file an annual return, it shall be punishable with fine which shall not be less than ![]() . 25000 but which may extend to
. 25000 but which may extend to ![]() .5,00,000. The designated partner of such limited liability partnership shall be punishable with fine which shall not be less than
.5,00,000. The designated partner of such limited liability partnership shall be punishable with fine which shall not be less than ![]() . 10,000 but which may extend to
. 10,000 but which may extend to ![]() . 1,00,000. Delayed filing will also lead to severe additional fees that increases to
. 1,00,000. Delayed filing will also lead to severe additional fees that increases to ![]() . 200 everyday
. 200 everyday
Legal Term
In forma pauperis
(in form-ah paw-purr-iss) adj. or adv. Latin for “in the form of a pauper,”a referring to a party to a lawsuit who gets filing fees waived by filing a declaration of lack of funds (has no money to pay). These declarations are most often found in divorces by young marrieds or poor defendants who have been sued.
MCA Updates
Companies (Incorporation) Third Amendment Rules, 2016 and Companies (Accounts) Amendment Rules, 2016 were notified on 27.07.2016 and will come in effect as on the date of publishing in the Official Gazette.
National Company Law Tribunal Rules, 2016 and National Company Law Appellate Tribunal Rules, 2016 were notified on 21.07.2016 and will come in effect as on the date of publishing in the Official Gazette.
Companies Share Capital and Debentures Third Amendment Rules, 2016 was notified on 19.07.2016 and will come in effect as on the date of publishing in the Official Gazette.
SEBI Updates
Revised Formats for Financial Results and Implementation of Ind AS by listed entities which have listed their debt securities and/or non-cumulative redeemable preference shares.
RBI Updates
- Implementation of Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS).
- Guidelines for Relief Measures by NBFCs in areas affected by Natural Calamities released.
- Master Direction – Lending to Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME) Sector
Income Tax Updates
- Amendment of the Income-tax Rules-seeking PAN details of trustees and others in case of registration of trusts – modifications of Form 10A under Rule 17A.


 '
'